This article picked by a teacher with suggested questions is part of the Financial Times free schools access programme. Details/registration here.
Read our full range of US High School economics picks here.
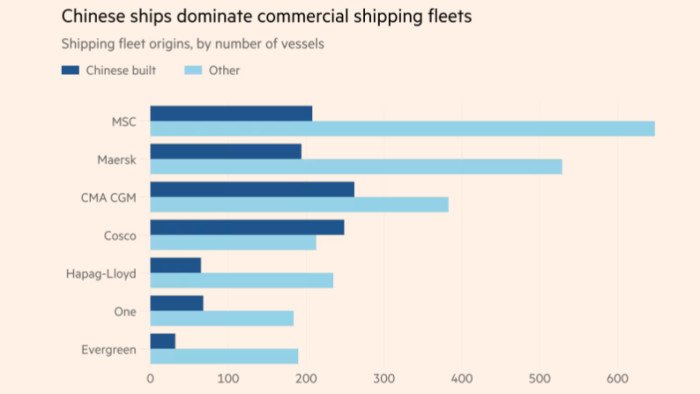
A proposed US tariff on Chinese-built ships — up to $1.5mn per docking — has alarmed the agricultural sector, which heavily relies on affordable shipping to maintain export competitiveness. Farmers warn that the increased transaction costs could crush profitability, drive up prices of imported inputs like fertiliser, and shift trade advantages to foreign competitors. The policy, intended to counter China’s maritime dominance, risks backfiring by distorting trade flows and undermining domestic producers.
Essential Question: How do tariffs and other trade barriers affect domestic producers and global market efficiency?
Read the FT article and then answer the questions below:
US farmers express dismay over proposal for levies on China-built ships
-
What are the intended goals of the proposed tariff on Chinese-built ships, and who is expected to bear the costs?
-
How do increased transportation costs function as a form of transaction cost in international trade?
-
In what ways could this proposal distort trade patterns between the US and its agricultural trading partners?
-
What role do input costs, like fertiliser, play in shaping the overall competitiveness of American agriculture?
-
How might the proposed US tariffs on Chinese-built ships affect the prices, profits and competitiveness of American agricultural exports in international markets?
-
Why is predictability in trade policy important for market participants like grain exporters and freight operators? Why is predictability in trade policy important for market participants like grain exporters and freight operators?
-
Comparative advantage refers to a country’s ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partners. It is one of the key components to global trade. How has China’s comparative advantage in shipbuilding contributed to its dominance in global shipping, and how might disrupting access to Chinese-built vessels affect the efficiency and cost structure of global trade?
-
How does this case illustrate the tension between economic nationalism and global market efficiency?
Joel Miller and James Redelsheimer, Foundation for Economic Education.
Click here for FEE FT Classroom Edition with classroom-ready presentations and suggested answers for teachers.